How to Kick Your Shared Services Implementation Into Gear
Add bookmarkWhat can shared services learn from the discipline of military operations? Microland's Anil Prem DSouza leverages the effectiveness he learned in the Indian Navy to the Business Shared Services implementation he heads at Microland. He aims to bring all support services up to speed to enable Microland's growth. Here, Anil shares the "tools of change" and the new ecosystem he has created.
Our organisation, a specialist in IT infrastructure services, recently entered into the world of Business Shared Services by initiating the integration of all our company’s support services into a single Shared Services team. The main objective of this project was to build an environment wherein all support services (i.e. HR, Finance, IT and Facilities) perform on par with the speed and agility of the business operations, thereby enabling the company to rapidly expand its business horizons.
The trigger that led to this initiative was the success of the HR Shared Services team in implementing a Shared Services model. The HR Shared Services operation was modelled on Six Sigma and ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)-based principles. Resulting self-service initiatives, HR process automations, and end-to-end onboarding projects increased the efficiency of the Business HR, HRSS and Talent Acquisition teams by more than 50%.
Tools of change
A network of Tools was developed to design and build an efficient and self-sustaining HR Shared Services:
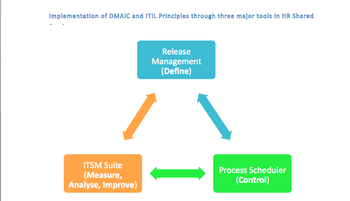
- Release Management: A SharePoint-based system wherein all Policies, Processes, Guidelines and FAQs are managed to ensure knowledge is never lost. All process documents were prepared with the DMAIC principle in mind. To ensure that controls are never lost, a mandatory process control section was introduced to every process document. Newer ways of managing this on Social Media – such as ‘Yammer’ – are also being explored. The success of this system is really down to the usage of simple and easy to use templates.
- Process Scheduler: The Process Scheduler is a central control system which manages all scheduled and unscheduled processes within the Shared Services. Scheduler tasks are based on the Release Management tool. This tool was built indigenously using MS Outlook, which is cost-effective and easy to access.
- ITSM Suite: The Case Management or the ITSM Suite tool is the heart of the Shared Services. The tool manages queries and employee issues as well as issues raised by the Shared Services team members themselves, if they come across a potential problem. The tool used is indigenously built on ITIL standards and customised to suit HR requirements. It has excellent features, such as live reporting, and enables ITIL lifecycle management by providing problem, change and knowledge management.
Successes achieved using the ecosystem
- The Shared Services team inculcated the habit of a ‘Project Way of Working’ instead of the earlier method of handling endless transactions.
- Adopting the newer way of working in HRSS not only brought control over accurate and swift delivery of HR Processes but actually helped the team in motivation and work life balance.
- The team could easily develop process documents (through Release Management), which exponentially increased the knowledge and control of the processes handled by them.
- Reduced attrition rate of the team in the past two years paved way for the formation of a high performance team.
- One of the reasons for nil attrition in the team was because work did not become mundane as newer projects with newer challenges motivated the team to be the change that they wanted to bring in the organization.
- Improved performance of connected teams such as recruitment, finance and facilities.
Figure 1: Implementation of DMAIC and ITIL Principles through three major tools in HR Shared Services

Transition
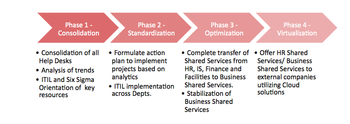
The transition plan of the Business Shared Services was segmented in four stages. Although the first stage of the plan has been successful, the team continues to face some challenges in moving ahead with the transition. Nevertheless, the core team continues to find pioneering ways to implement the change.
|
Current Challenge |
Challenge Description |
Short Term Workaround |
|
IT Support |
Immediate automation of ERP systems due to slow pace from IT teams. |
Utilizing internal resources to create simple tools to automate the process.
Ex: Use of Excel Macros to create workflow based user forms. |
|
Change Management |
Change Management is a major challenge as teams working with prevailing systems have apprehensions to newer technology and systems. |
Persistent approach of enabling change in teams by persuading via success stories of improvements in HR systems and processes. |
Roadmap for the future
Figure 2: Roadmap
Conclusion
The above case study is a live example of an organization’s evolution from an archaic and stagnant position to a resilient and dynamic workforce, capable of functioning seamlessly in tandem with constantly changing technology.
The project is still live and is making good progress as per the project schedule. When completed, the project will enable the support functions of the company to partner with operations in its quest to achieve the company’s business goals – and support functions will not be seen as an impediment to growth.
[eventpdf]





















